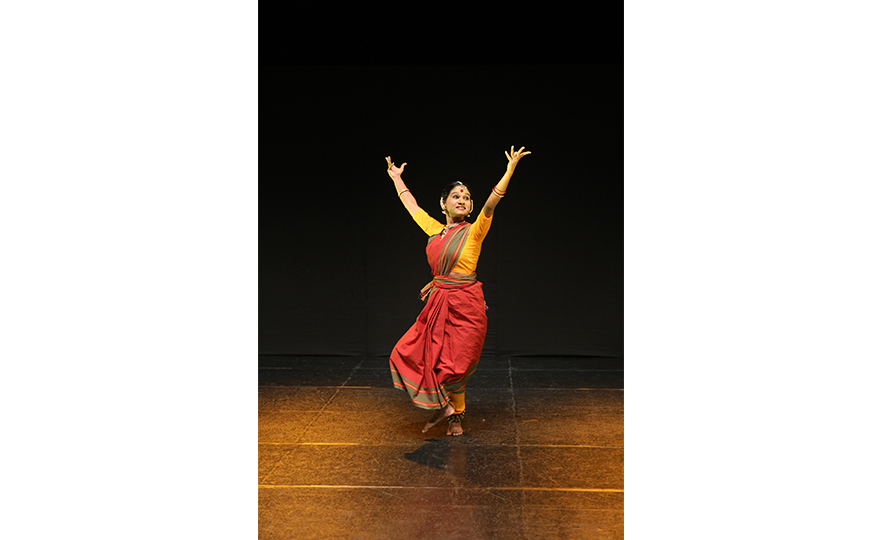
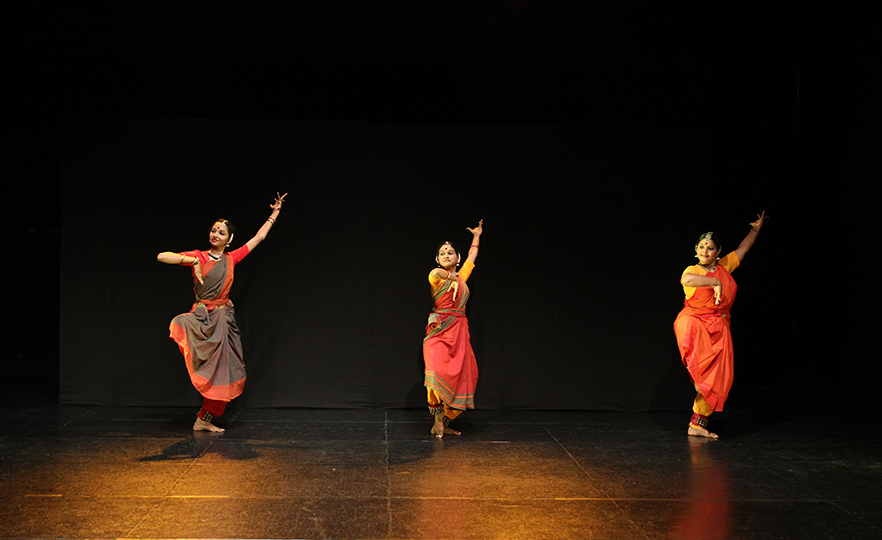
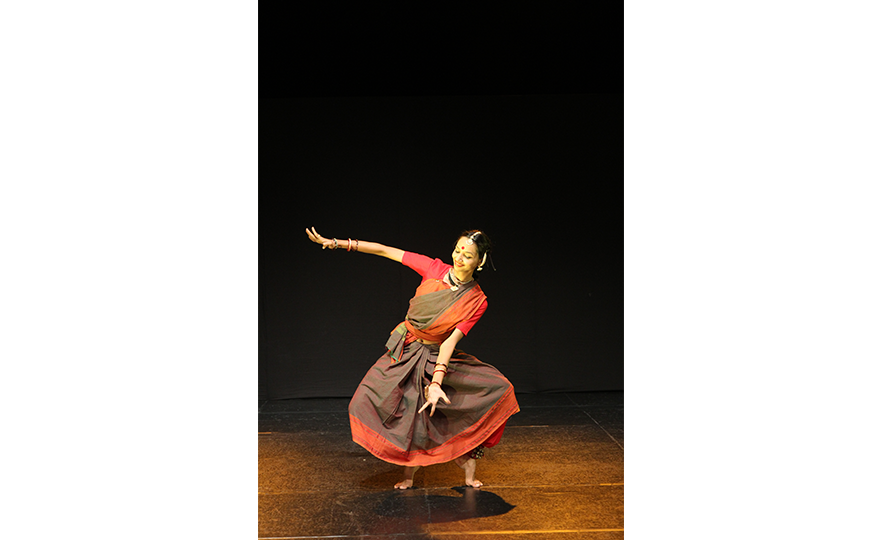
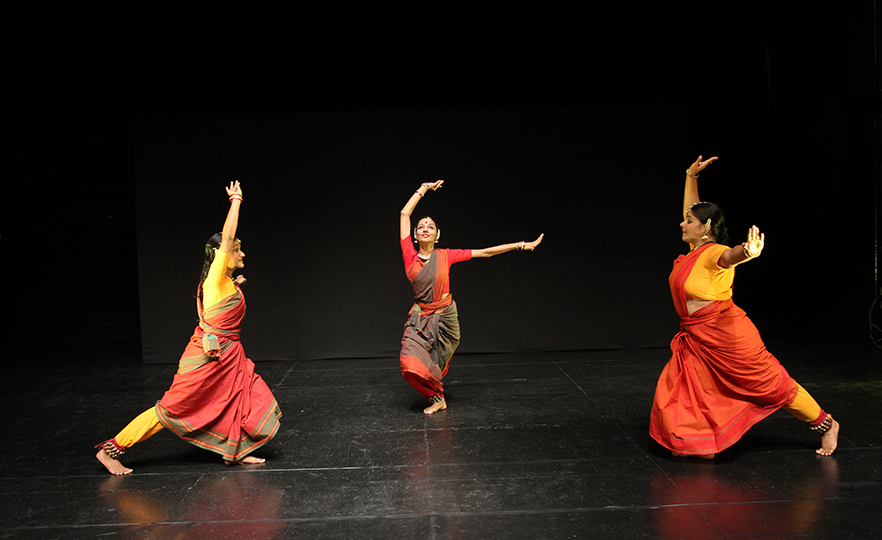
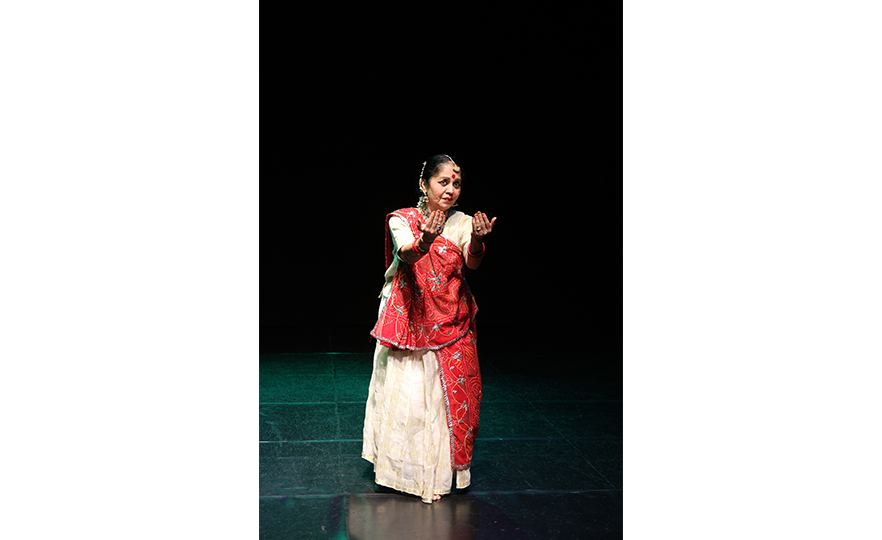
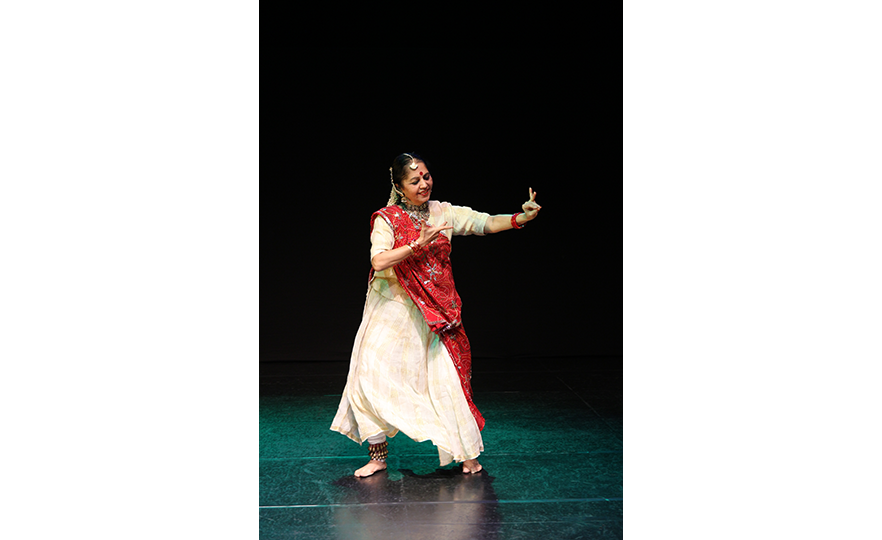
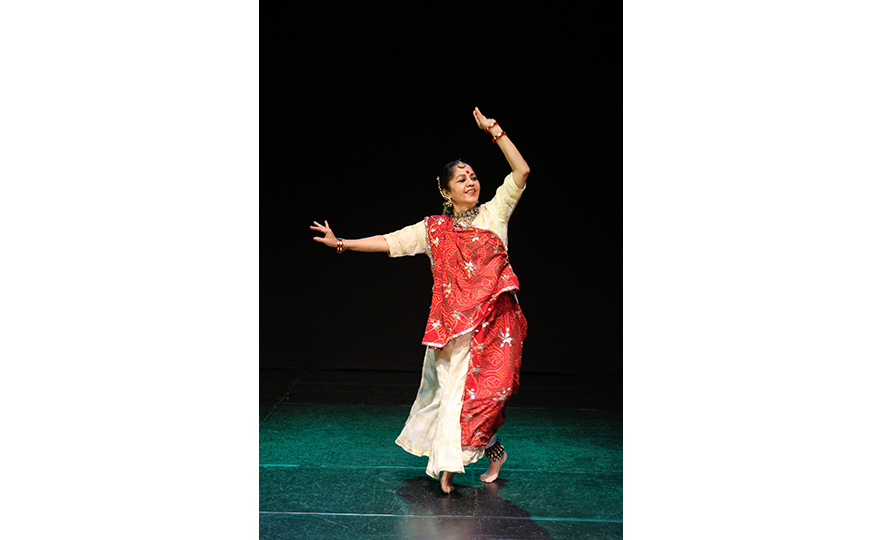
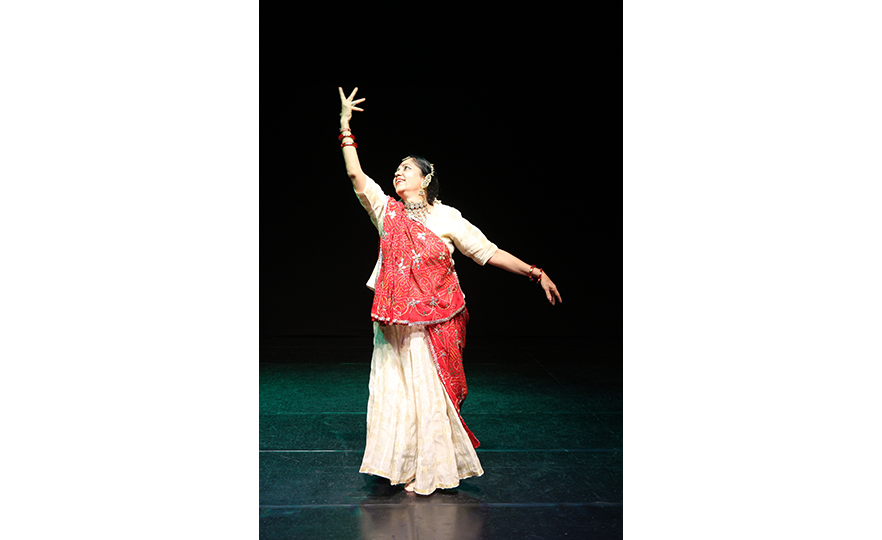
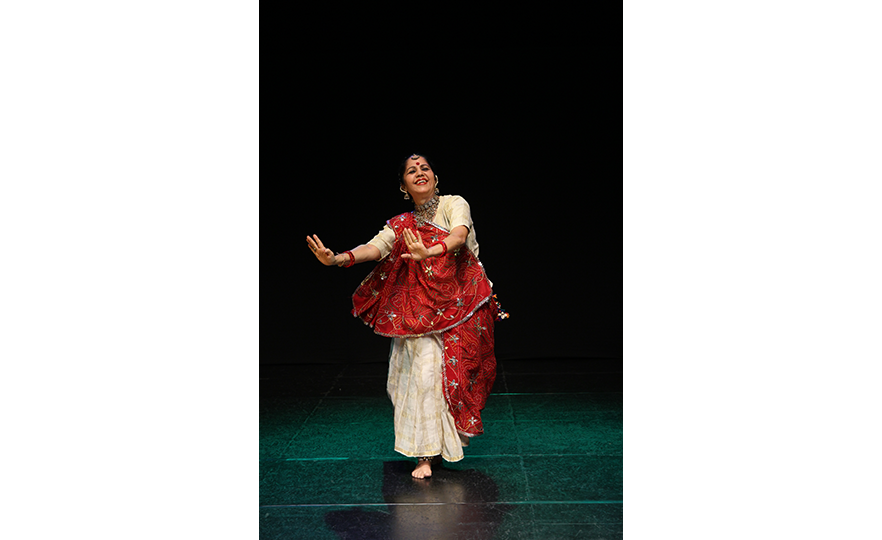
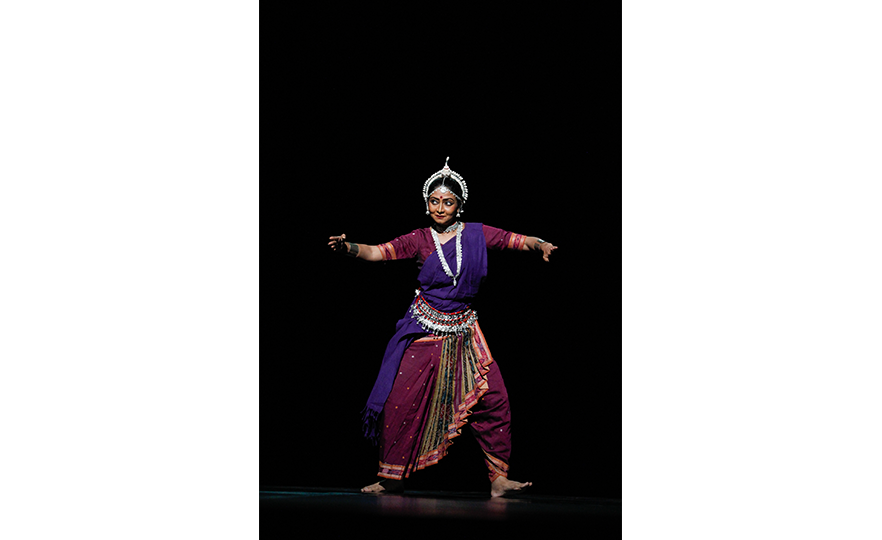
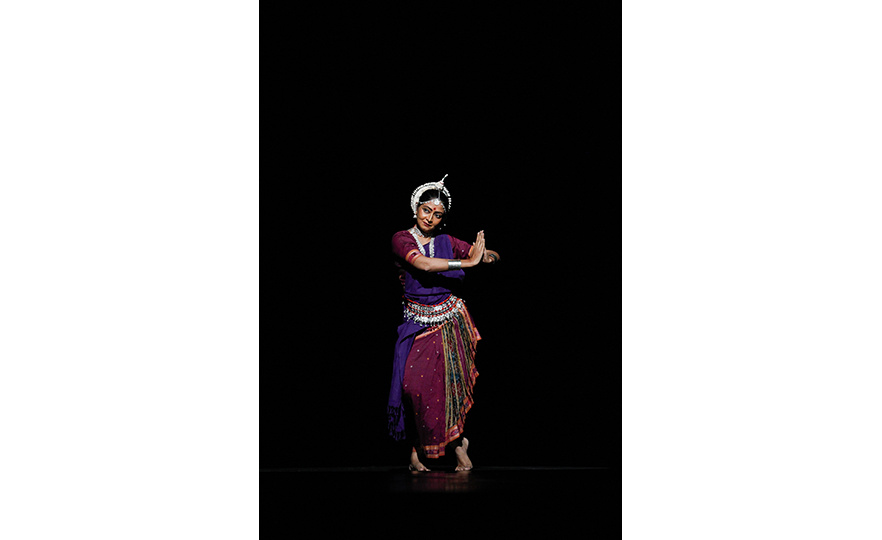
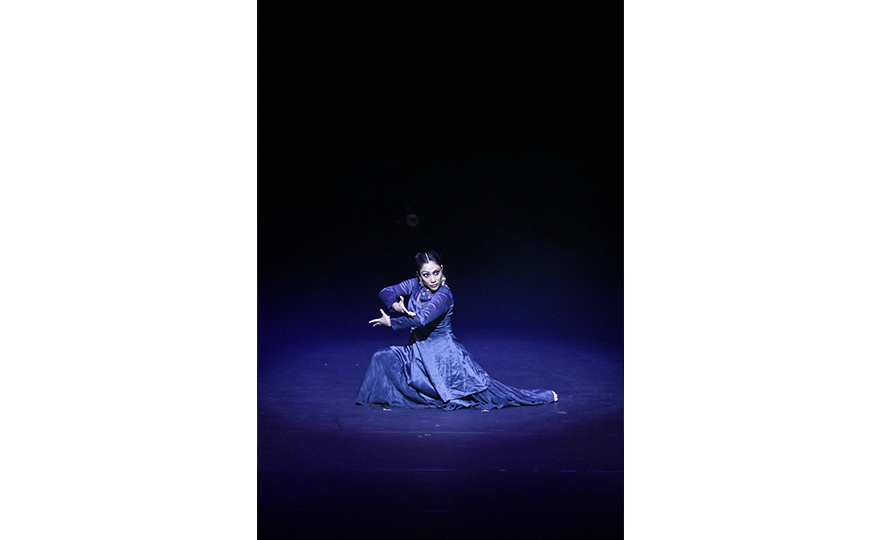
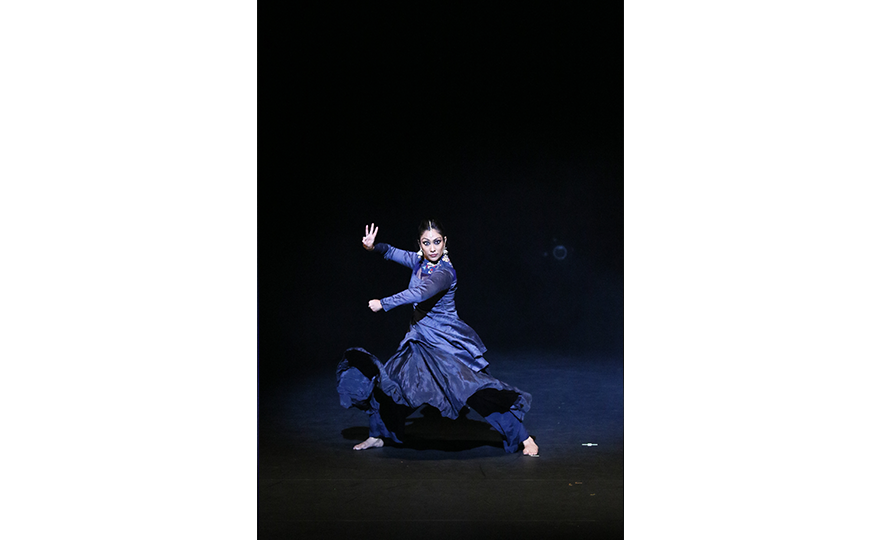
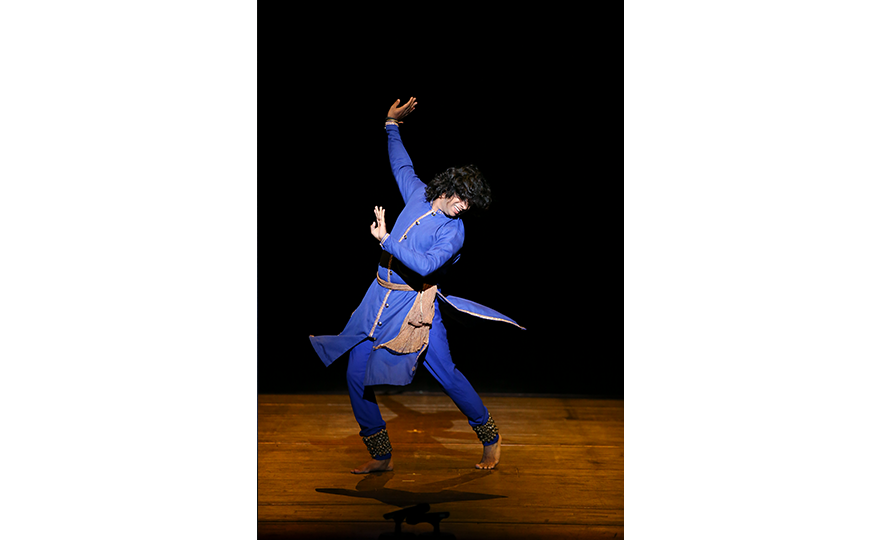
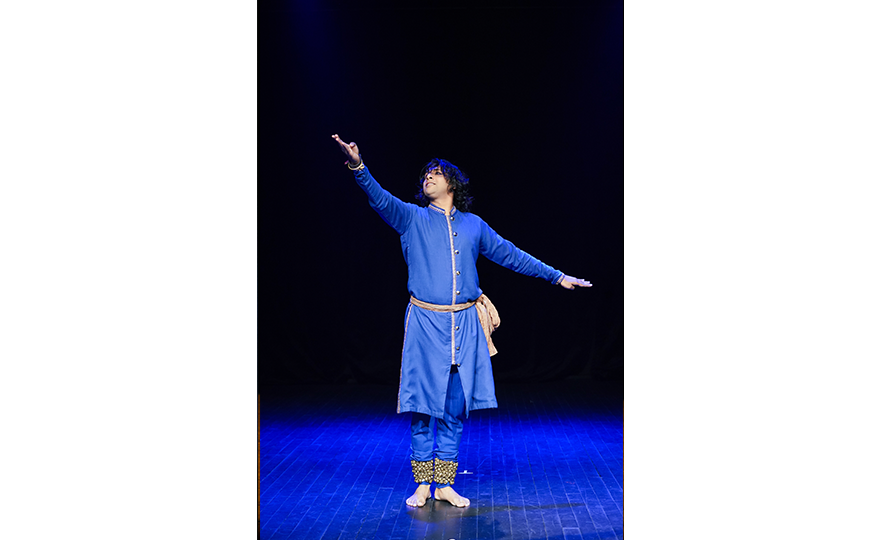
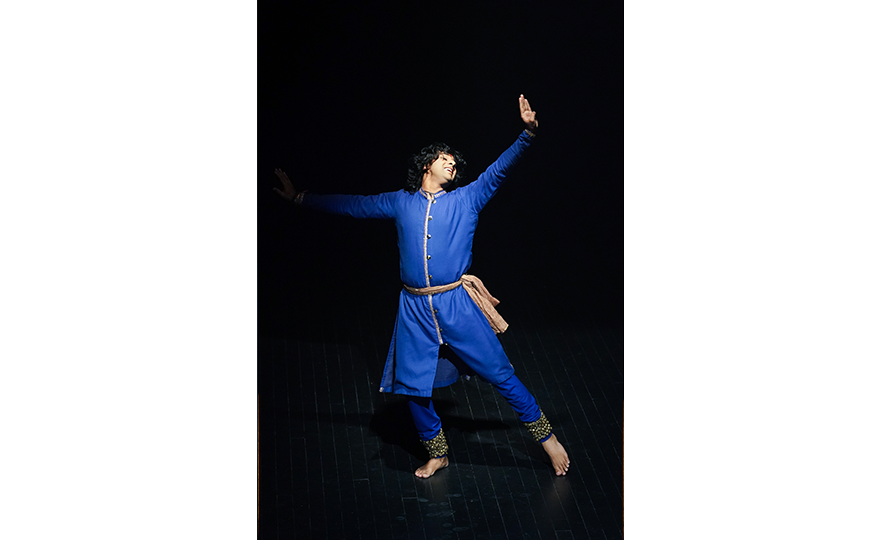
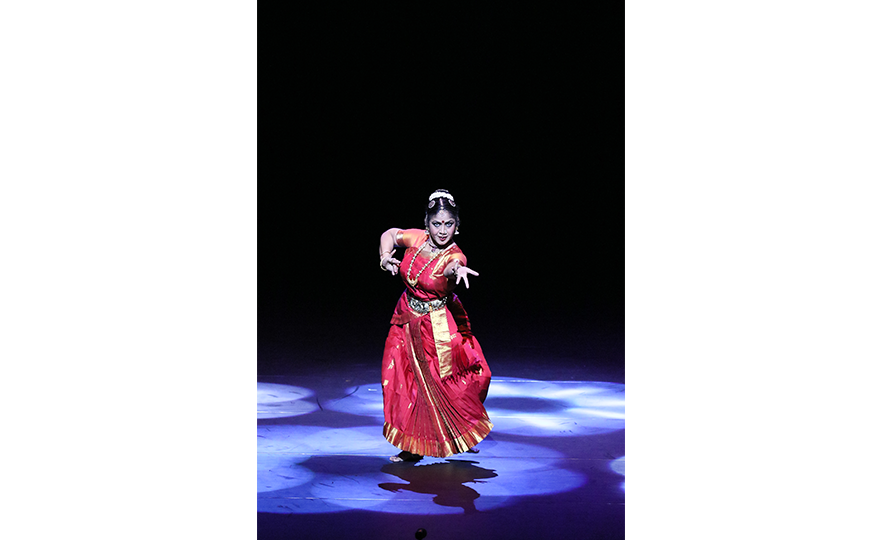
Bharatanatyam-Jatis Waram
India∙Tamil Nadu
- Performer
- Divya Jay Pitel, Radhika Nemina
- Date of Performance
- Sep 26, 2011
- Characteristics
- ∙One of the 8 major traditional dances recognized by the Indian government
∙Originates from a religious dance performed by Devadasi female dancers in Hindu temples
- Artistic director
- Parul Shah:Professor of Dance at University of Baroda. PhD in Gujarat Classical Dance. Completed 6 years of study at University of Wisconsin on ballet, modern dance, labanotation, history of dance and critique.
Awarded Contributions to Gujarat Award at Baroda Para in 2011. Received certificate of honor from Ayutthaya Rajabhat University in 2010. Received certification of honor from Madhya Pradesh state in 2009 for contributions to performing arts.
- Choreographer
-

Jatis Waram is the second sequence in the Bharatanatyam, a dance comprising 7 sequences. Bharatanatyam is the oldest dance in India, originating from a religious dance performed by female dancers (Devadasis) for the gods in Hindu temples. Like majority of Indian traditional dances, it is based on a religious narrative. Although it used to be performed by a single female dancer, it is now common for 2 or more dancers or male dancers to participate in the dance.
Bharatanatyam is characterized by its powerful rhythms. Dancers execute complex steps and detailed hand gestures (mudra) while keeping the upper body still and bending the legs or placing the heel down on the floor. The rhythms of the ghungroo (bell instrument worn on the ankles) further elevates the mood. The dancer delivers the message of the dance through highly controlled facial expressions down to the movements of the eyebrows and eyes.
Bharatanatyam was an esoteric art form until the 20th century as it was traditionally performed only in temples. Today, it is taught in many schools and organizations, acting as a source of artistic inspiration in all genres of Indian art, from music to songs, poetry, painting and sculpture.
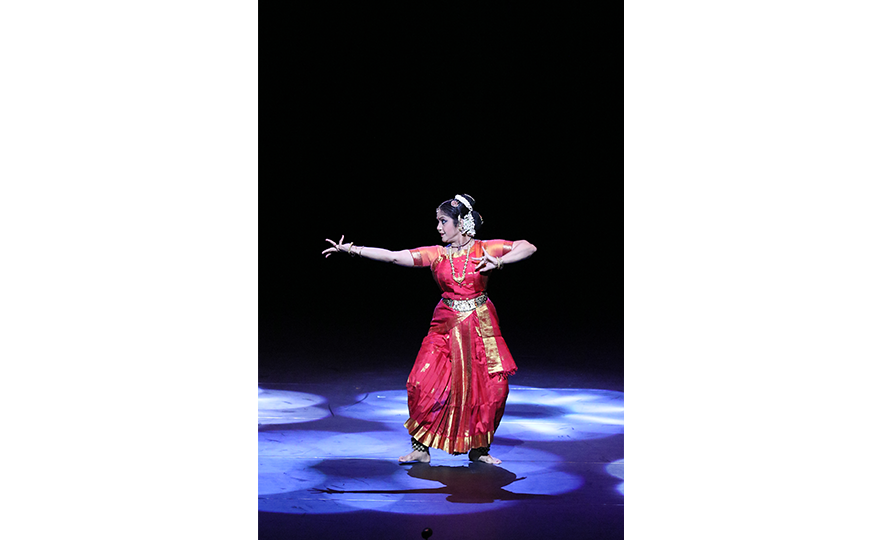
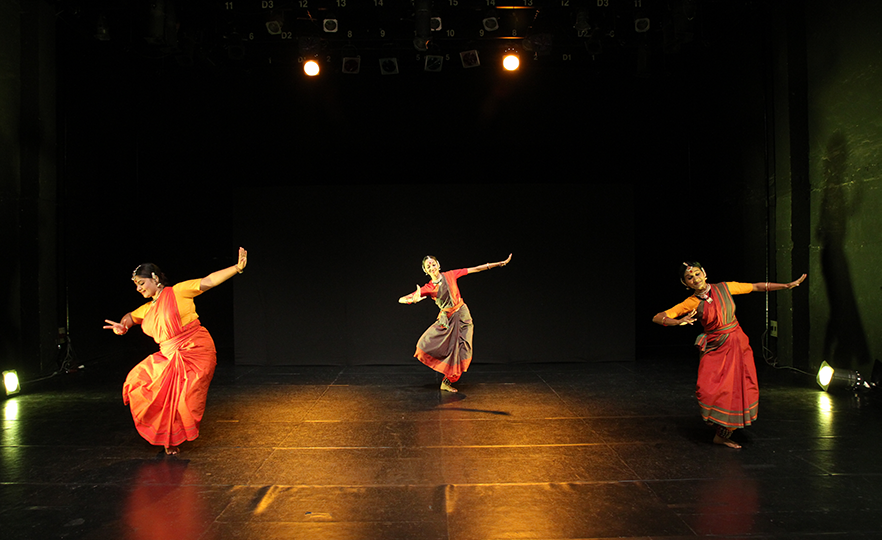
Bharatanatyam-Padam
India∙Tamil Nadu
- Performer
- Parul Shah
- Date of Performance
- Sep 26, 2011
- Characteristics
- ∙4th sequence in the Bharatanatyam, one of the 8 major traditional dances recognized by the Indian government
∙Only performed by female dancers
- Artistic director
- Parul Shah:Professor of Dance at University of Baroda. PhD in Gujarat Classical Dance. Completed 6 years of study at University of Wisconsin on ballet, modern dance, labanotation, history of dance and critique.
Awarded Contributions to Gujarat Award at Baroda Para in 2011. Received certificate of honor from Ayutthaya Rajabhat University in 2010. Received certification of honor from Madhya Pradesh state in 2009 for contributions to performing arts.
- Choreographer
-
Padam is the second sequence in the Bharatanatyam, a dance comprising 7 sequences. It is an expression of worship, humility, and a solemn spiritual message or religious prayer.
- Performer
- Papia Desai
- Date of Performance
- Oct 2, 2013
- Characteristics
- ∙One of the 8 major traditional dances recognized by the Indian government
∙Originates from a religious dance performed by Devadasi female dancers in Hindu temples
- Artistic director
- Papia Desai2nd generation choreographer of the Indian Revival Group. Daughter of Yog Sunder, founder, director and choreographer of the Indian Revival Group and follower of Tagore and Ghandi’s philosophy. Participated in many Indian public TV productions and international forums.
- Choreographer
- Papia Desai
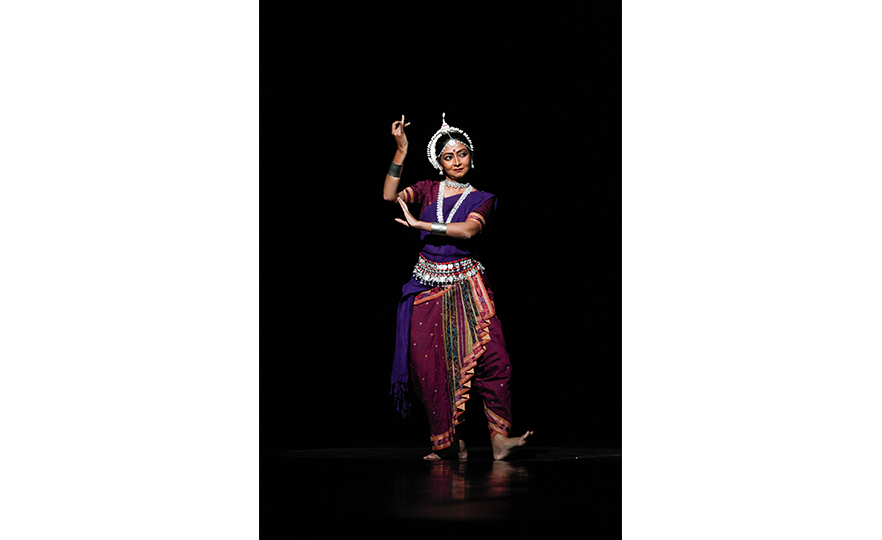

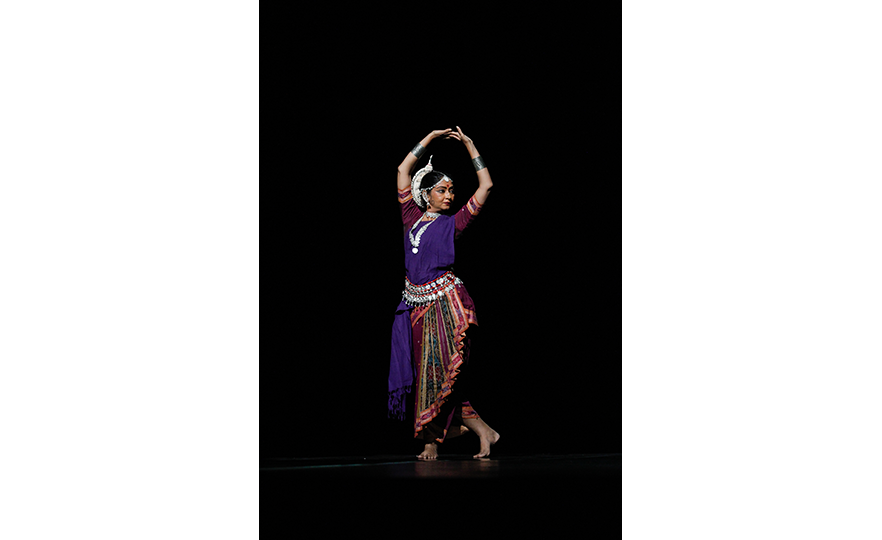
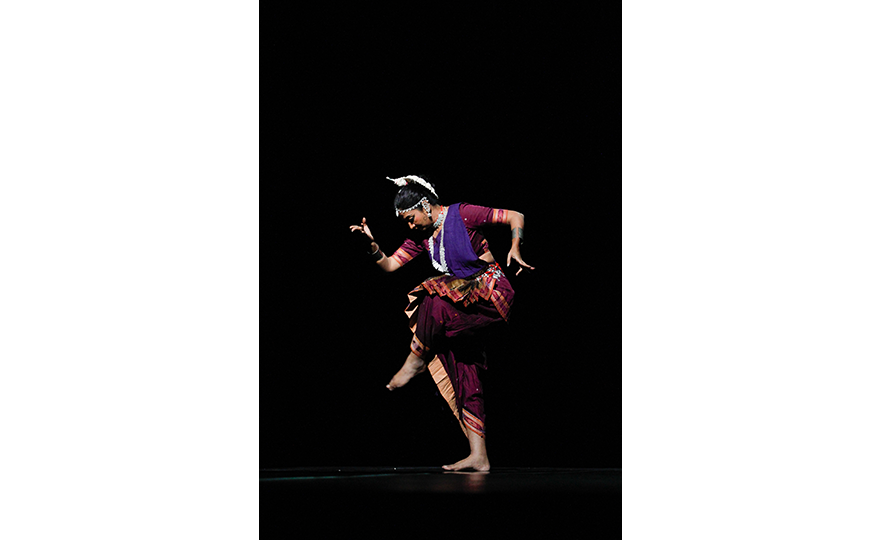
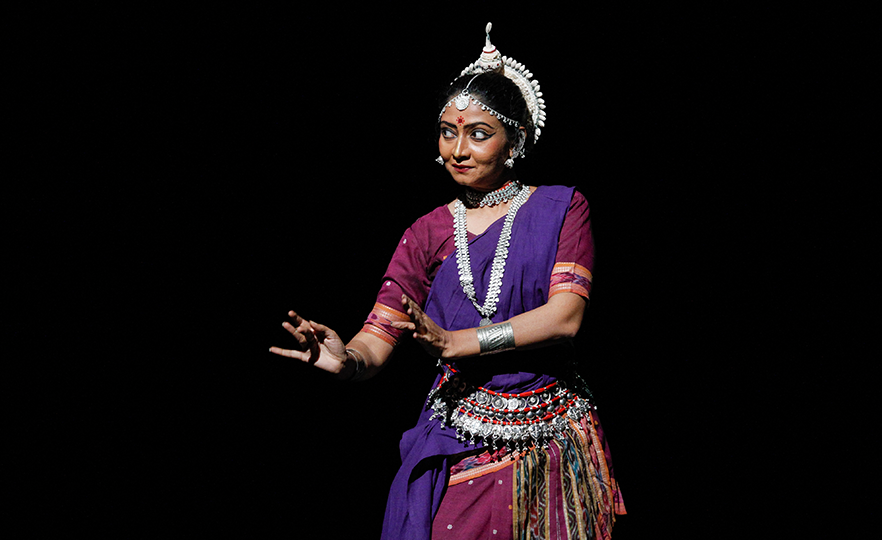
Odissi, a dance which developed in the East Indian state of Orissa is rooted in the dances performed by temple dancers (devadasi). It is usually performed by a solo female dancer, who acts out all the roles in legends from ancient epics. In the modern day, it may be performed together by 2 or more dancers. The Odissi dance depicts stories about the 8 incarnations of the Hindu god Vishnu, expressing deep love and strong faith in him.
The detailed expressiveness of Odissi is comparable to that of Bharatanatyam, a traditional dance from the South Indian region. Its movements are restrained in scale, and a half-sitting posture with the legs bent at the knees is maintained during the dance. Unlike Khattak which involves the stretching of the arms, the arms remain curved in Odissi and there are over 50 different traditional hand gestures. The head, chest and torso are used to accentuate femininity, and the curves of the dance are emotive and sensual. The movements of the eyes and facial expressions are highly important. It is one of the oldest dances in India together with Bharatanatyam.
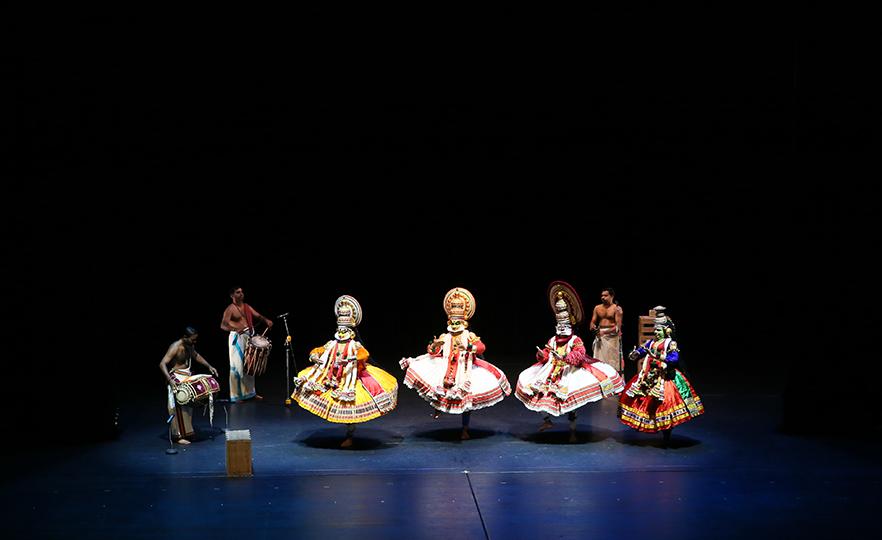
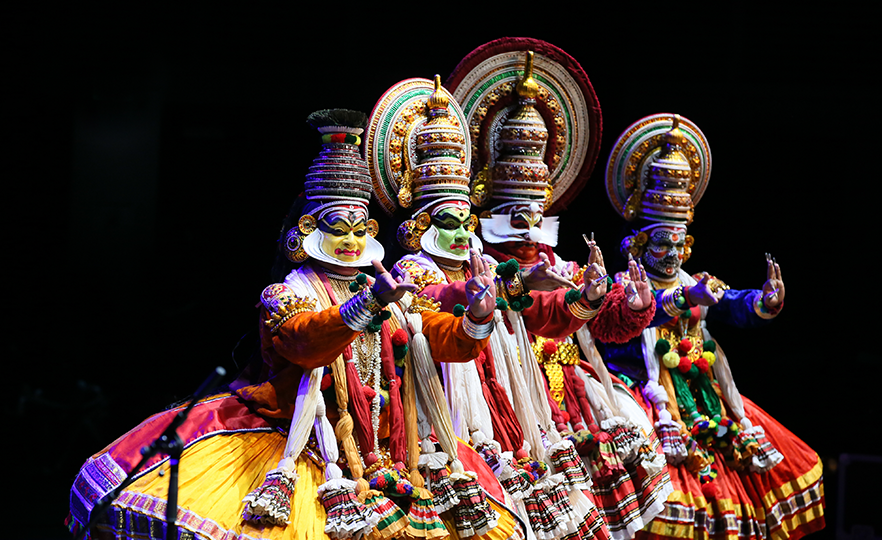
Kathakali - Daksha Yaagam
India∙Kerala State
- Performer
- Kallekulangara Kathakali Foundation
- Date of Performance
- Sep 3, 2016
- Characteristics
- ∙One of the 8 major traditional dances recognized by the Indian government
- Artistic director
-
- Choreographer
- P.N.VentikattaramanRepresentative of the Kallekulangara Kathakali Foundation, obtained master’s degree at Kerala Kalamandalam (2010), performing the Kathakali all across India, Europe, Northern Europe, Southeast Asia, United Arab Emirates etc.
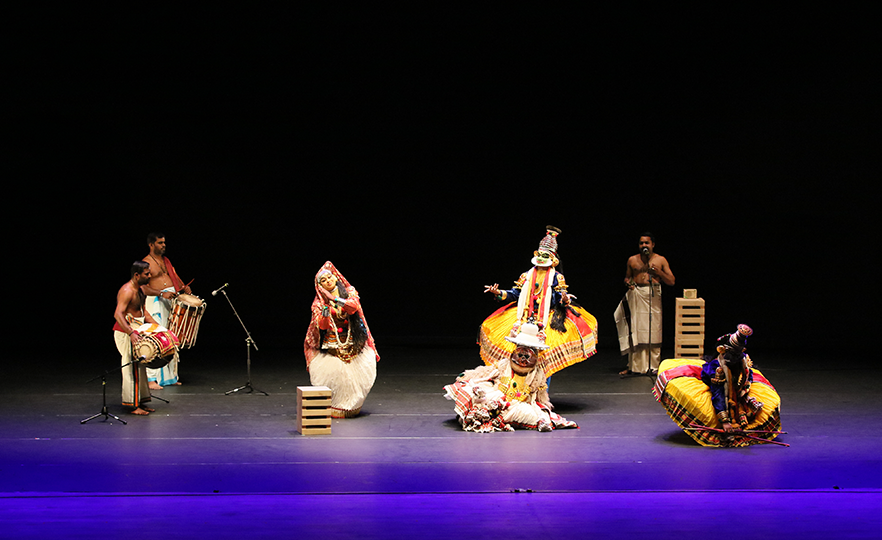

This is a dance in the Kathakali tradition, one of the 4 major traditional dances of India, based on the story of Daksha Yaagam, about King Daksha, father of Sathi, wife of Shiva. Kathakali is a traditional art form dating back 600 years, originating from Kerala State in Southwest India in the 17th century. It is a comprehensive theatrical performance combining dance, theatre, music, makeup and costumes in a cohesive whole. Just like the Bharatanatyam, the Kathakali is a religious play in which the performer recites stories in the form of poetry and expresses it through dance and acting. The plot of Kathakali dances are based on traditional stories such as the epics of Mahabharata, Ramayana and Shaiva which form the roots of inspiration in Indian culture. At the core of the aesthetics of Indian dance is the purpose of oneness with the supernatural or rasa.
Kathakali performances begin at 6 pm in outdoor stages and carry on until morning the next day. Thus, it requires great physical and mental strength, and only dancers who have gone through the toughest training are allowed to perform. Traditionally, the dance was performed only by men and male dancers played women’s roles as well. Although it was a form of high culture, only performed in the royal courts in the 17th century, it is now widely enjoyed by the general public.
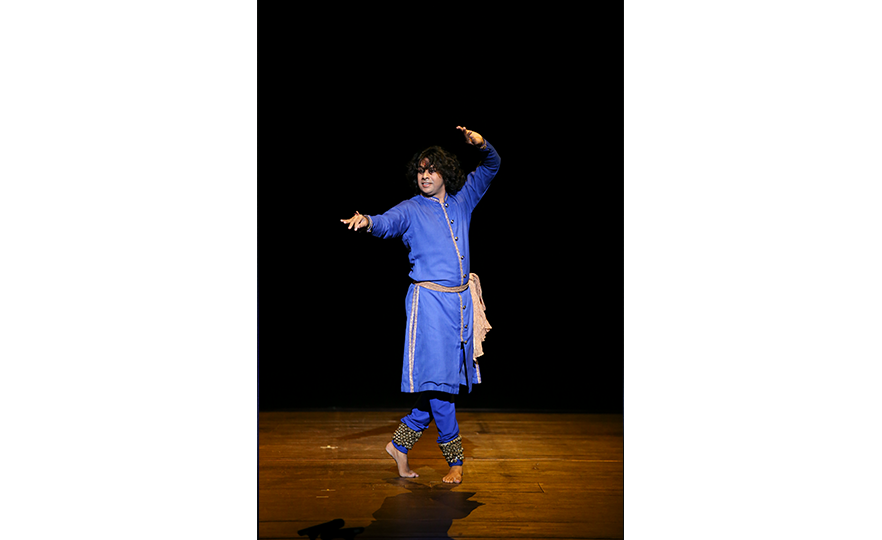
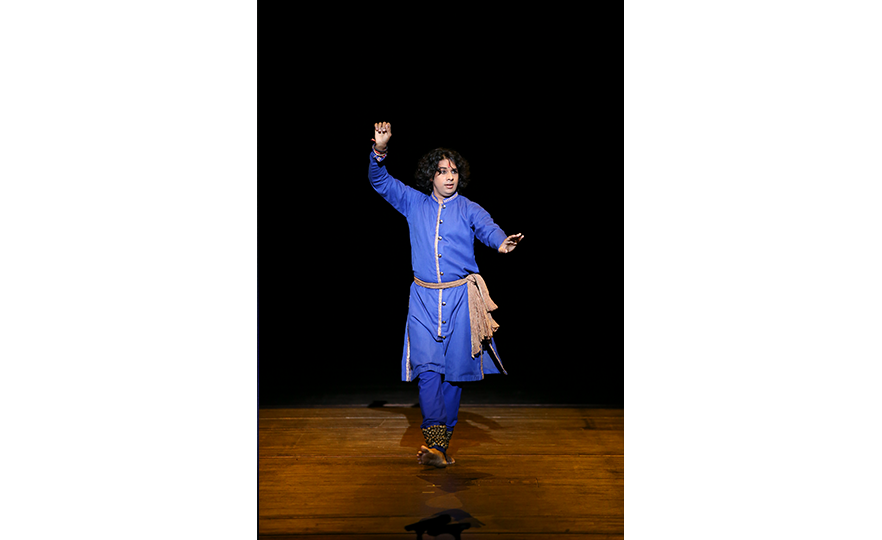
Kathak
India∙Northern India
- Performer
- Amit Khinchi
- Date of Performance
- Aug 27-28, 2017
- Characteristics
- ∙One of the 8 major traditional dances recognized by the Indian government
∙Uses the ghungroo (a bell instrument worn around the ankle)
- Artistic director
-
- Choreographer
- Amit Khinchi∙Born to a line of Kathak practitioners, succeeded the dance from his father, Ghanshyam Khinchi.
∙Became a disciple of Rajendra Kumar Gangani
∙Graduated from the National Institute of Kathak Dance (Kathak Kendra) in 2010
∙Full scholarship in university
∙Recipient of Indian Ministry of Culture scholarship for 2 years-Majored in Kathak at the Khairagarh University in India
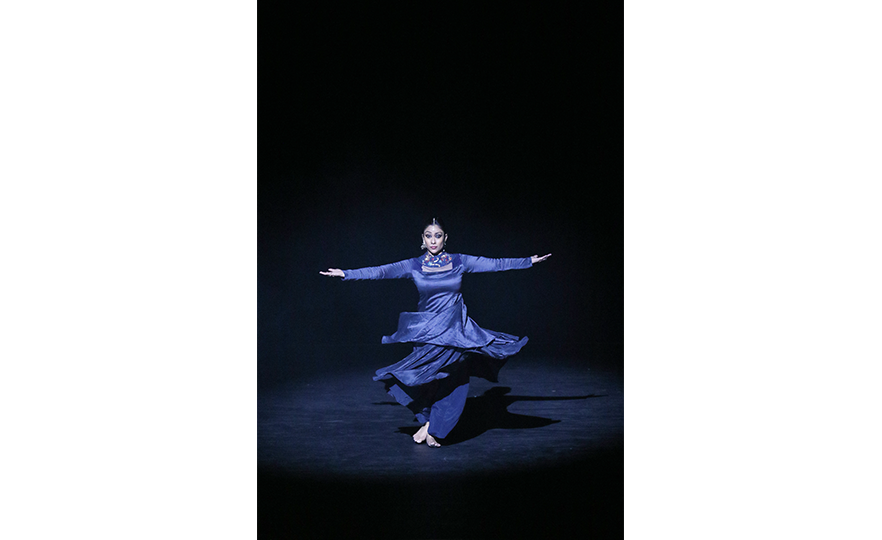

Kathak is a beautiful and elegant dance which expresses stories through elaborate hand movements and steps. It can be performed by both male and female dancers, and it is called the ‘dance of love’ as it is often performed together by men and women. Dancers wear ghungroo (bell instrument worn on the ankles) on both ankles and dance to the tabla (small drums played in pairs) and sitar (traditional stringed instrument with 18-21 strings). The relentless rhythm of the ghungroo heightens the excitement in the atmosphere, while the quick steps called ‘tatkar’ and spins executed to the fast paced rhythms are elaborate, sophisticated and full of energy.
In ancient Hindu temples, storytellers used to tell legends through song, music and dance. The name 'Kathak' is derived from the sanskrit word ‘katha’ which refers to the professional art of storytelling, and ‘karhakas’, which means ‘storyteller’. Kathak originated in Northern India in the 3rd to 4th century BC, and was transmitted as a form of puja (prayer ritual) until the 15th century, when it developed into a dance for court banquets under the influence of Persia and the Mughal empire.
Tarangam Kuchipudi
India∙Southwest Krishna
- Performer
- Ananda Shankar Jayant
- Date of Performance
- Sep 2, 2015
- Characteristics
- ∙One of the 8 major traditional dances recognized by the Indian government
- Artistic director
- Sanjukta SinhaKathak artist, disciple of Kathak dancer Arjun Mishra, holds Kathak workshops all over the world, as well as joint performances with international modern dance groups // Ananda Shankar Jayant / Traditional indian dancer (Bharatanatyam and Kuchipudi), choreographer, dance critic, dance theorist Recipient of the Padma Shri Award and Sangeet Natak Akademi Award
- Choreographer
-
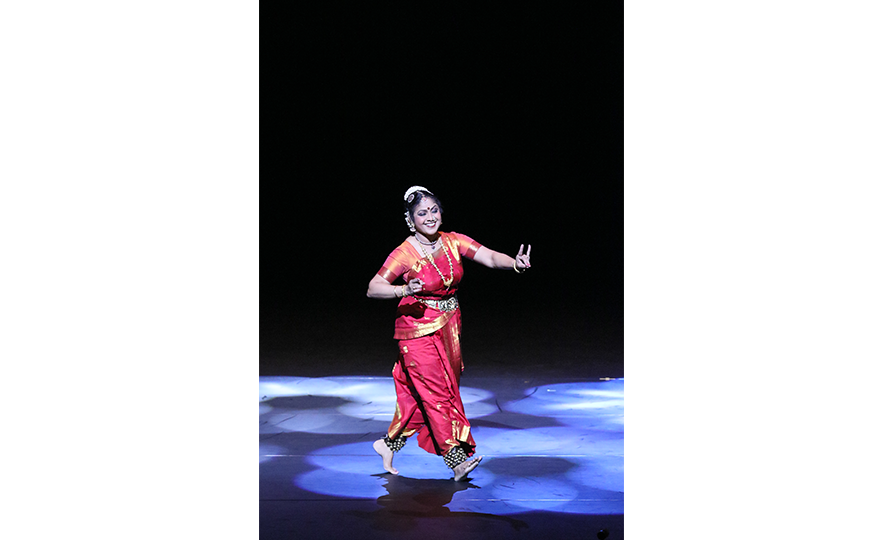

Traditionally, Kuchipudi was performed at night in Hindu temples or by the light of a fire, for people returning home after a long time. It is characterized by fast paced steps in time to the rhythm and sculptural poses. While it was traditionally performed only by Brahmin (priests), with men performing female roles as well, it is now performed mainly by female dancers.
Tarangam is the most popular repertoire in the Kuchipudi dance-drama tradition, which demonstrates an extremely high level of skill. The almost acrobatic movements of the dance contain philosophical metaphors for the heavy responsibilities of life. The Kuchipudi dance is rooted in the Natya Shastra, an ancient Sanskrit Hindu text, while the name Kuchipudi originates from the Kuchelapuram village in the Southern Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. Although Kuchipudi was frequently performed up to the middle ages (15th-16th century), it suffered a decline following the muslim invasion. Later in the early 17th century, it spread across the entire region of India. During the European colonial era, traditional Indian religion and culture was suppressed by Christian missionaries, and the dance suffered the indignity of being treated as a vulgar dance performed by prostitutes. It was revived in the 1920s through the effort of experts who worked to restore the traditional dances of India.